Confirming its expertise in active hair ingredients, Seppic completes its hair care offering with an ingredient designed to make hair naturally more beautiful: XYLISHINE™C
The "skinification" trend reveals the growing influence of skin care habits on hair and scalp care needs. Seppic has created XYLISHINE™ C, an active ingredient that acts globally on the repair of the scalp and hair cuticles. Thanks to XYLISHINE™ C, hair becomes visually more beautiful with increased shine, better curl definition and volume control.
A request for hair and scalp caring
Beautiful hair is a result of a healthy scalp and restored hair fibers. Consumers are increasingly aware of the link between hair quality and scalp health. 93% of Chinese hair care consumers are aware that scalp care can improve the appearance and health of their hair.1 In the past, scalp care was mainly limited to anti-dandruff solutions. Today, scalp care is more widely recognized as a form of skin care, with expectations for scalp balance and health.
Regarding the hair fiber, the “skinification” trend leads to new textures and hair care routines influenced by skin care claims and active ingredients. For example, hair hydration is one of the main concerns. Compared to skin care, we could define it by an aspect linked to cuticle health and hair fiber integrity (including roughness). To have “hydrated” hair fibers, moisture is needed to fill the gaps in the cuticle and to repair it.
To answer to this care need both for scalp and hair, XYLISHINE™ C (Xylitylglucoside, Anhydroxylitol, Maltitol, Xylitol, Pelvetia Canaliculata Extract) is a natural active derived from a patented complex of sugar derivatives renowned for their moisturizing effectiveness in skin care – combined with a bio-inspired algae harvested in France (Brittany), Pelvetia canaliculate, recognized for its exceptional resistance to dehydration. Compliant with Chinese IECIC and IECSC regulations, XYLISHINE™ C is also COSMOS and Natrue approved with a naturalness rating of 99.7% according to ISO 16128.
A scalp and hair restorer
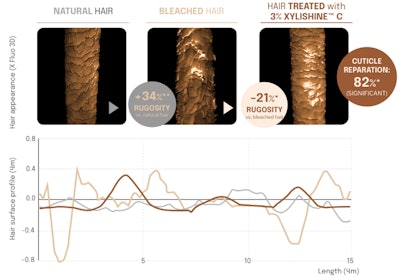
The cuticle is the layer of the hair fiber most exposed to a variety of environmental stresses & damages. It constitutes a barrier that protects the cortex from degradation. Maintaining the integrity of the cuticle is therefore the key to healthy & shiny hair. XYLISHINE™ C helps smooth cuticles and repair the surface appearance of damaged cuticles while restoring hair and water interactions. Seppic has measured the surface state of the keratin cuticles by XFluo 3D technology and found that Xylishine™ C significantly counterbalances the increased rugosity in hair caused by bleaching, restoring it to nearly that of natural hair: 82% reparation efficacy.3
Thanks to this mode of action, XYLISHINE™ C increases the shine of all hair types, curly or straight (+7%)4; curls are better defined (+16%),4 and hair is softer to the touch (+7%).4 XYLISHINE™ C is also effective in different climates (tested ex vivo in standard and extreme conditions of temperature and humidity) for visible anti-frizz action and volume control.
1 KuRunData/Mintel, November 2020, Décembre 2021
2 In vivo test on 20 male and female volunteers applying a shampoo containing 3% Xylishine™ C or a placebo shampoo for 28 days.
3 Ex vivo test applying a 3% solution of Xylishine™ C to healthy and damaged hair
4 In vivo test on two groups of volunteers with curly or straight hair applying a leave-on or a shampoo containing 3% Xylishine™ C or placebo
Disclaimer:
The above paid-for content was produced by and posted on behalf of the Sponsor. Content provided is generated solely by the Sponsor or its affiliates, and it is the Sponsor’s responsibility for the accuracy, completeness and validity of all information included. Cosmetics & Toiletries takes steps to ensure that you will not confuse sponsored content with content produced by Cosmetics & Toiletries and governed by its editorial policy.